Evolution
Evolution is one of the 5 top controls of sustainably successful corporate management. Under Evolution we summarize all innovations, inventions, and further developments, which change processes and structures in such a way that an enterprise can adapt sustainably and successfully to environmental changes.
Innovations and further developments can be divided into the main groups internal and external:
-
- External: Invent, develop and deliver new products and services for existing customers and new markets. The main drivers are the wishes and requirements of existing and potential customers.
- Internal: Improvements to adapt internal processes to new requirements from the various environmental spheres. This is intended to improve the company’s viability and competitiveness. The main drivers are end-to-end process integration and increasing internal effectiveness (doing the right things) and efficiency (doing the right things right).
The internal actors of innovation and development are the representatives of all functional areas. Divided again into external and internal, the following main functions emerge:
-
- External: Research and Development, Sales, Product Management, Production Planning, Information Technology, Procurement.
- Internal: Human Resources, Information Technology, Controller, Procurement, Accounting.
Innovation and development intentions are mostly implemented in projects because:
-
- We have never done that before!
- Experts from different functional areas have to contribute to find solutions.
- Often the projects cause high investment amounts and costs.
- The results must be available quickly and be implementable.
Project management must therefore clearly define responsibilities and accountabilities.
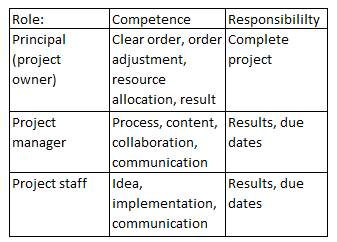
These responsibilities and accountabilities also apply in agile projects. This form of organization is recommended if there are constant changes in a project with regard to the task because the result to be achieved cannot yet be definitively defined at the beginning or the end product is not yet apparent (cf. mictrotool.de/wissen-online).
Evolutive developments arise in different subject areas
Functional-area-related development topics include:
-
- Completely IT-supported sales and distribution,
- Electronic purchasing from the search of potential suppliers to ordering and payment,
- Cross-company online exchange of production data and technical details on inspection processes,
- Batch tracking to localize the origin of a defect, and
- Improved data security.
Many environmental changes also lead internally to new developments:
Social environment,
-
- Flexible working hours, part-time work,
- Work@home, and
- Management of persons not present.
Technological environment:
-
- Collaborative Robots (COBOTS),
- Autonomous driving, drones, smart products,
- Cable cars instead of roads and subways,
- Designer medicines, and
- Low-CO2 agriculture.
The example of IBM is a good illustration of evolution as a driver of corporate development. After World War II, IBM became the world’s largest computer manufacturer. The worldwide breakthrough of personal computers was also achieved by IBM, although at that time many senior IBM managers could not even imagine the need for PCs. Today, the company produces supercomputers, but its main revenues come from business consulting, software rental and cloud services.
Evolution in the environments is therefore an essential topic in the management control system of sustainably successful companies.
